
JavaScript Asynchronous Module Definition (AMD) Explained Pluralsight
Object JavaScript - Asynchronous Module Definition (AMD) - AzureDays Object JavaScript - Asynchronous Module Definition (AMD) Posted on April 8, 2014 by Bruce D Kyle In the last few posts we showed how you can create objects in JavaScript. You can define public and private functions, methods, properties in your objects. But what about dependencies?
Definition Of Asynchronous Module (AMD) Mix With Marketing
As you mentioned, Closure is tightly-coupled. It does NOT use AMD. Therefore, the Closure Library is designed to be "modular" (similar to Dojo) but not "loose-coupling". Dojo from 1.6 onwards will be AMD-style loosely-coupled, although it will continue to have a global "dojo" object for backwards compatibility until 2.0. - Stephen Chung.

Why, What and Where Moodle’s AMD. Moodle is it still alive? Yes, and… by Alexandr Berezhnyk
This page talks about the design forces and use of the Asynchronous Module Definition (AMD) API for JavaScript modules, the module API supported by RequireJS. There is a different page that talks about general approach to modules on the web. Module Purposes § 1 What are JavaScript modules? What is their purpose?

Asynchronous module definition Alchetron, the free social encyclopedia
AMD is a module definition system that attempts to address some of the common issues with other systems like CommonJS and anonymous closures. AMD addresses these issues by: Registering the factory function by calling define (), instead of immediately executing it
Definition Of Asynchronous Module (AMD) Mix With Marketing
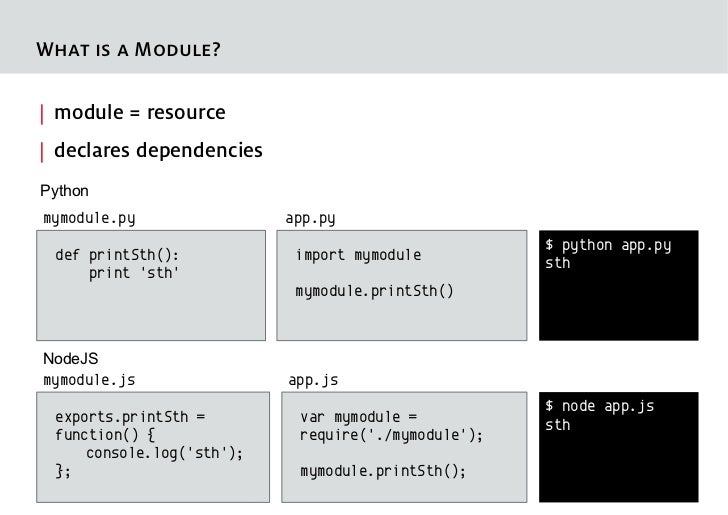
We will take the example of the ko.bindingHandlers.hasFocus example from the binding handlers documentation. By wrapping that handler in it's own module you can restrict it's use only to the pages that need it. The wrapped module becomes: define ( ['knockout-x.y.z'], function(ko) {. ko.bindingHandlers.hasFocus = {.

不是前端却革命了前端腾讯云开发者社区腾讯云
This is simply because it is an asynchronous process, in terms of actual processing, and will not block the browser from running events/JS, rendering the page, et cetera. Share Improve this answer

Dojo Asynchronous Module Definition (AMD)
Regarding AMD (Asynchronous Module Definition ) I read the phase like this: The AMD format comes from wanting a module format that was better than today's "write a bunch of script tags with implicit dependencies that you have to manually order" and something that was easy to use directly in the browser.

Module, Package, Workspace
About AMD : async module definition However, if the same module system is used in the browser, each require statement would need to trigger an HTTP request to the server. This is an order of magnitude slower and less reliable than a file system access call.

Asynchronous Module Definition (AMD)
This course, JavaScript Asynchronous Module Definition (AMD) Explained, starts with a simple web project that grows into a comprehensive pattern suitable for use in your own projects.
SAPUI5 Programming for Beginners Part 1 Start coding in SAPUI5
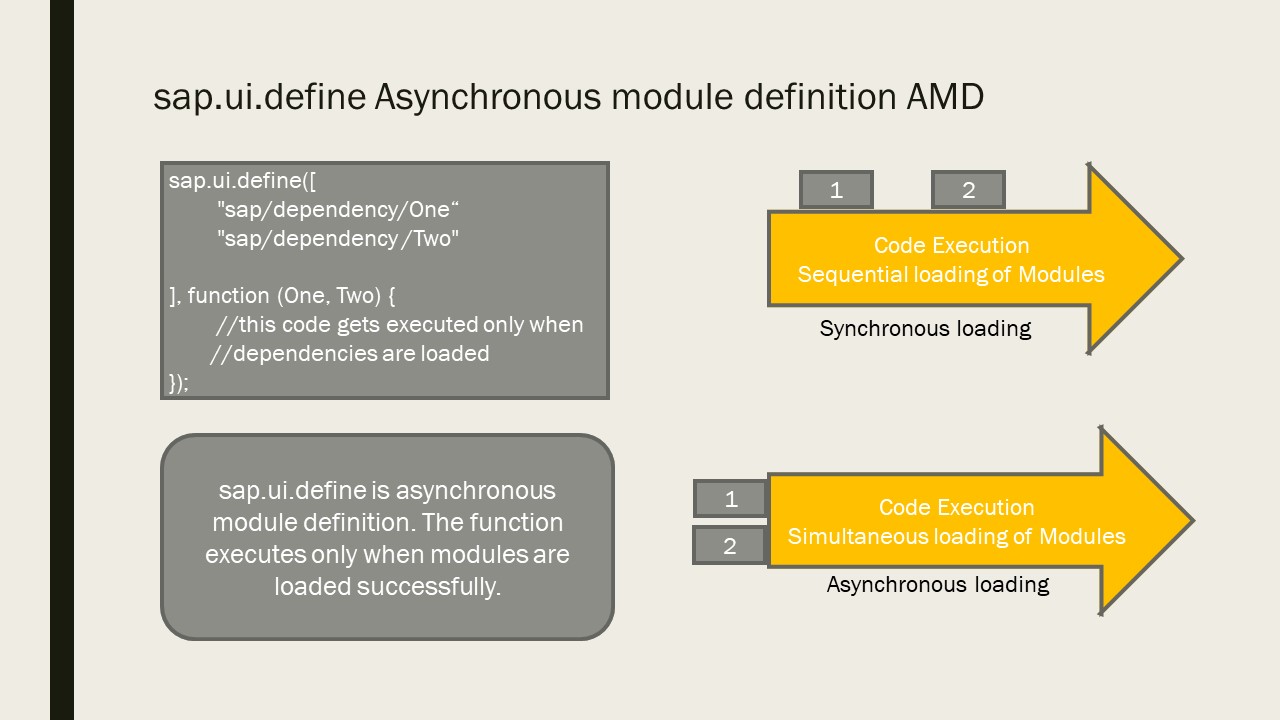
AMD (Asynchronous Module Definition) For the browser, designed to load modules asynchronously. Uses define and require. For an AMD example: define ( ["moduleA", "moduleB"], function (moduleA, moduleB) { return someFunction; }); UMD (Universal Module Definition) Tries to unify CJS and AMD, making modules work in both client and server.
34 Asynchronous Module Definition Javascript Tutorial Modern Javascript Blog
The Asynchronous Module Definition API specifies a mechanism for defining modules such that the module and its dependencies can be asynchronously loaded. This is particularly well suited for the browser environment where synchronous loading of modules incurs performance, usability, debugging, and cross-domain access problems.

38 Asynchronous Module Definition Javascript Tutorial Javascript Nerd Answer
The Asynchronous Module Definition (AMD) format is the module format that Dojo adopted starting with Dojo 1.7. It provides many enhancements over the legacy Dojo module style, including fully asynchronous operation, true package portability, better dependency management, and improved debugging support.

Asynchronous Module Definition (AMD)
AMD: The Asynchronous Module Definition. The primary building block for referencing and defining modular JS code. require: An API for the require () function that allows dynamic, asynchronous loading of modules, and for resolving some module ID-based strings to file paths.

𝗔𝘀𝘆𝗻𝗰𝗵𝗿𝗼𝗻𝗼𝘂𝘀 𝗺𝗼𝗱𝘂𝗹𝗲 𝗱𝗲𝗳𝗶𝗻𝗶𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻, 𝗘𝗦𝟲 𝘆 𝗖𝗼𝗺𝗺𝗼𝗻𝗝𝗦 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝘂𝗹𝗲𝘀 (𝗝𝗮𝘃𝗮𝗦𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁 𝗣𝗮𝗿𝘁𝗲 𝗜𝗜𝗜.𝟮) 📥🧰🚀 YouTube
Asynchronous module definition (AMD) is a specification for the programming language JavaScript. It defines an application programming interface (API) that defines code modules and their dependencies, and loads them asynchronously if desired. Implementations of AMD provide the following benefits:
Asynchronous Module Definition (AMD) used for Dependency Injection (D…
Javascript - Asynchronous Module Definition (AMD) About The AMD 1) 2) specifies a mechanism for defining modules such that: the module and its dependencies can be specified and loaded asynchronously. 3) ie Both the module and dependencies can be asynchronously loaded. API: Import / Export
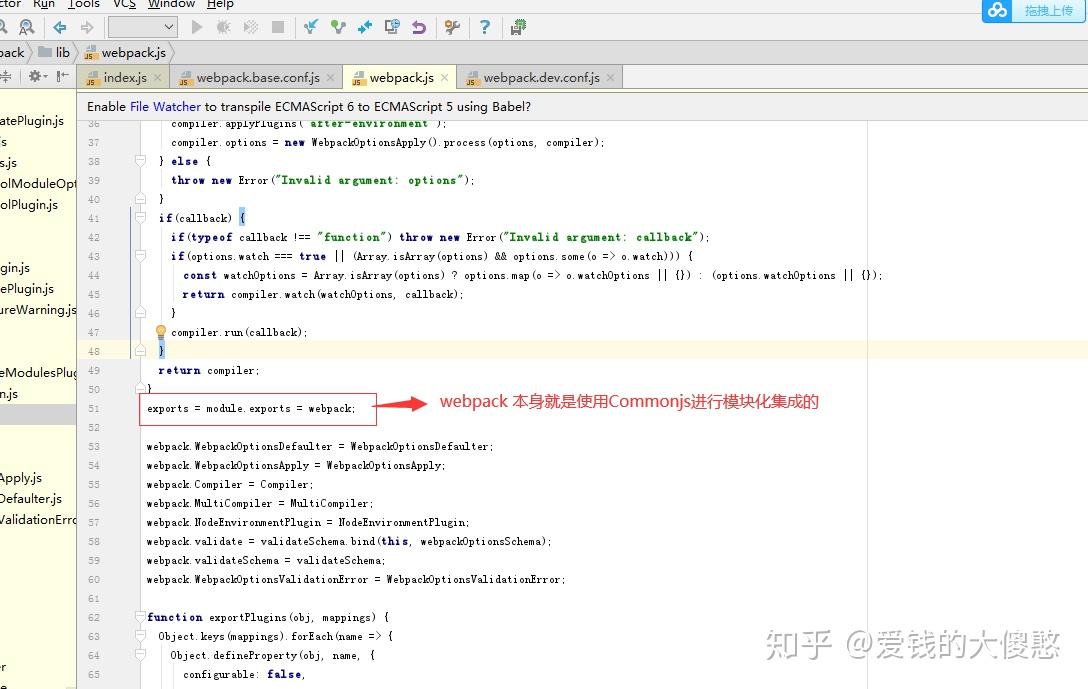
ES6 的模块化 知乎
AMD, which stands for Asynchronous Module Definition, is a module format that allows developers to define modules and their dependencies in a JavaScript application. The AMD format was designed to make it easier to manage large and complex JavaScript applications, and to make it easier for developers to work with external libraries and frameworks.